If you need to hide All Site Content links for unprivileged users, follow the steps shown below.
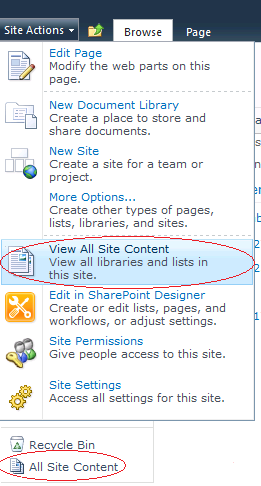
Your application’s master page is to be modified. If you use a built-in master page (for example, v4.master for 2010 or default.master for 2007), I recommend to create a full copy of the built-in one and deploy it. These steps are described in the article SharePoint: How to create a custom master page.
In the master page, locate all places where _layouts/viewlsts.aspx is pointed out. You’ll likely find several controls (for example, a MenuItemTemplate, a SPLinkButton and so on), which render All Site Content links one way or another. These controls can be divided into three groups described below.
The controls exposing the PermissionsString property
The controls expose such opportune property as PermissionsString defining a permission set the user must have in order to see the content the controls provide. For this group of controls PermissionsString is likely set by default to ViewFormPages. That is, if the user has permission to view forms, views and application pages, and enumerate lists, he will have access to All Site Content links displayed by these controls. So, set PermissionsString to ManageWeb in order that the links in question would be visible only for users able to perform administration tasks for the Web site (e.g. content managing, features activating and deactivating and so on). For example, within your copy of v4.master you’ll definitely run into such controls as MenuItemTemplate and ClusteredSPLinkButton declared as follows:
<SharePoint:SiteActions id="SiteActionsMenuMain" runat="server" ...>
<CustomTemplate>
<SharePoint:FeatureMenuTemplate ID="FeatureMenuTemplate1" runat="server" ...>
...
<SharePoint:MenuItemTemplate runat="server"
id="MenuItem_ViewAllSiteContents"
Text="<%$Resources:wss,quiklnch_allcontent%>"
Description="<%$Resources:wss,siteactions_allcontentdescription%>"
ImageUrl="/_layouts/images/allcontent32.png"
MenuGroupId="300"
Sequence="302"
UseShortId="true"
ClientOnClickNavigateUrl="~site/_layouts/viewlsts.aspx"
PermissionsString="ViewFormPages"
PermissionMode="Any" />
...
</SharePoint:FeatureMenuTemplate>
</CustomTemplate>
</SharePoint:SiteActions>
The control represents an item in the drop-down Site Actions menu.
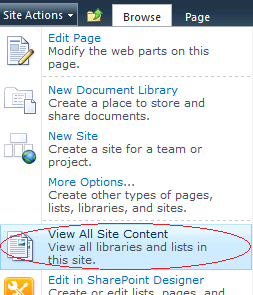
Another control is ClusteredSPLinkButton
<asp:ContentPlaceHolder id="PlaceHolderQuickLaunchBottom" runat="server">
...
<SharePoint:UIVersionedContent id="PlaceHolderQuickLaunchBottomV4" UIVersion="4" runat="server">
<ContentTemplate>
<ul class="s4-specialNavLinkList">
...
<li>
<SharePoint:ClusteredSPLinkButton
id="idNavLinkViewAllV4"
runat="server"
PermissionsString="ViewFormPages"
NavigateUrl="~site/_layouts/viewlsts.aspx"
ImageClass="s4-specialNavIcon"
ImageUrl="/_layouts/images/fgimg.png"
ImageWidth=16
ImageHeight=16
OffsetX=0
OffsetY=0
Text="<%$Resources:wss,quiklnch_allcontent_short%>"
accesskey="<%$Resources:wss,quiklnch_allcontent_AK%>"/>
</li>
</ul>
</ContentTemplate>
</SharePoint:UIVersionedContent>
</asp:ContentPlaceHolder>
The control represents a link in the Quick Launch Bar.
So, change the PermissionsString property of the above controls to ManageWeb.
The controls, which are wrapped in a SPSecurityTrimmedControl
The controls lies in SPSecurityTrimmedControl. SPSecurityTrimmedControl renders the content it contains (Html or other controls) depending on the current user’s permissions. It exposes the same PermissionsString property. Thus, set the property to ManageWeb. Within a master page based on v4.master there is a SPLinkButton surrounded by the SPSecurityTrimmedControl, see the following markup:
<asp:ContentPlaceHolder id="PlaceHolderQuickLaunchTop" runat="server">
<SharePoint:UIVersionedContent UIVersion="3" runat="server">
<ContentTemplate>
<h3 class="ms-standardheader">
...
<Sharepoint:SPSecurityTrimmedControl runat="server" PermissionsString="ViewFormPages">
<div class="ms-quicklaunchheader">
<SharePoint:SPLinkButton id="idNavLinkViewAll"
runat="server" NavigateUrl="~site/_layouts/viewlsts.aspx"
Text="<%$Resources:wss,quiklnch_allcontent%>"
accesskey="<%$Resources:wss,quiklnch_allcontent_AK%>"/>
</div>
</SharePoint:SPSecurityTrimmedControl>
</h3>
</ContentTemplate>
</SharePoint:UIVersionedContent>
</asp:ContentPlaceHolder>
Here the SPLinkButton represents the All Site Content link in the Quick Launch Bar as well, but it’s displayed for applications migrated from SharePoint 2007 with the previous version of UI. So, set the PermissionsString of the surrounding SPSecurityTrimmedControl to ManageWeb.
All other controls
The controls from the last group are not wrapped in SPSecurityTrimmedControl and don’t provide any ability to limit the access to their contents for unprivileged users. What is needed to do is put such controls into SPSecurityTrimmedControl and set the PermissionsString property of the last to ManageWeb. Within your copy of v4.master there are a few such controls:
<Sharepoint:UIVersionedContent runat="server" UIVersion="3">
<ContentTemplate>
<Sharepoint:SPNavigationManager id="TreeViewNavigationManager" runat="server" ...>
<table class="ms-navSubMenu1" ...>
<tr>
<td>
<table class="ms-navheader" ...>
<tr>
<td nowrap="nowrap" id="idSiteHierarchy">
<SharePoint:SPLinkButton runat="server" id="idNavLinkSiteHierarchy"
NavigateUrl="~site/_layouts/viewlsts.aspx"
Text="<%$Resources:wss,treeview_header%>"
accesskey="<%$Resources:wss,quiklnch_allcontent_AK%>"/>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
...
</Sharepoint:SPNavigationManager>
</ContentTemplate>
</SharePoint:UIVersionedContent>
Here the All Site Content link is presented by SPLinkButton. It’s displayed under Quick Launch, when the previous version of UI is enabled and when the TreeView navigation option is turned on in Site Settings. Wrap the link into SPSecurityTrimmedControl. It may look like the following:
<Sharepoint:UIVersionedContent runat="server" UIVersion="3">
<ContentTemplate>
<Sharepoint:SPNavigationManager id="TreeViewNavigationManager" runat="server" ...>
<SharePoint:SPSecurityTrimmedControl ID="SPSecurityTrimmedControl2"
runat="server" PermissionsString="ManageWeb">
<table class="ms-navSubMenu1" ...>
<tr>
<td>
<table class="ms-navheader" ...>
<tr>
<td nowrap="nowrap" id="idSiteHierarchy">
<SharePoint:SPLinkButton runat="server" id="idNavLinkSiteHierarchy"
NavigateUrl="~site/_layouts/viewlsts.aspx"
Text="<%$Resources:wss,treeview_header%>"
accesskey="<%$Resources:wss,quiklnch_allcontent_AK%>"/>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</SharePoint:SPSecurityTrimmedControl>
...
</Sharepoint:SPNavigationManager>
</ContentTemplate>
</SharePoint:UIVersionedContent>
Another control is declared as SPLinkButton too:
<Sharepoint:UIVersionedContent runat="server" UIVersion="4">
<ContentTemplate>
<Sharepoint:SPNavigationManager id="TreeViewNavigationManagerV4" runat="server" ...>
<SharePoint:SPLinkButton runat="server" id="idNavLinkSiteHierarchyV4"
NavigateUrl="~site/_layouts/viewlsts.aspx"
Text="<%$Resources:wss,treeview_header%>"
accesskey="<%$Resources:wss,quiklnch_allcontent_AK%>"
CssClass="s4-qlheader" />
...
</Sharepoint:SPNavigationManager>
</ContentTemplate>
</SharePoint:UIVersionedContent>
It’s a link in the treeview under Quick Launch, when the TreeView Navigation option is enabled in Site Settings. It can be modified to the following:
<Sharepoint:UIVersionedContent runat="server" UIVersion="4">
<ContentTemplate>
<Sharepoint:SPNavigationManager id="TreeViewNavigationManagerV4" runat="server" ...>
<SharePoint:SPSecurityTrimmedControl ID="SPSecurityTrimmedControl3"
runat="server" PermissionsString="ManageWeb">
<SharePoint:SPLinkButton runat="server" id="idNavLinkSiteHierarchyV4"
NavigateUrl="~site/_layouts/viewlsts.aspx"
Text="<%$Resources:wss,treeview_header%>"
accesskey="<%$Resources:wss,quiklnch_allcontent_AK%>"
CssClass="s4-qlheader" />
</SharePoint:SPSecurityTrimmedControl>
...
</Sharepoint:SPNavigationManager>
</ContentTemplate>
</SharePoint:UIVersionedContent>
Summary
Let’s sum up. If you see a control exposing PermissionsString, set the property to ManageWeb. If a control is within a SPSecurityTrimmedControl, set the PermissionsString of the last one to ManageWeb as well. And finally, if it’s just a control, add a new SPSecurityTrimmedControl, place the first one in it and set the ManageWeb permission.